Research on termites in urban areas: approaches and gaps

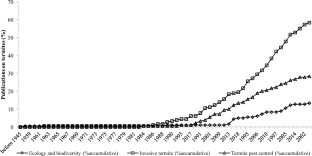
Termites comprise a large group of organisms in urban areas, and this leads us to believe that there is a comprehensive literature on the subject, sufficient for conducting a systematic review of the last years. Consequently, the aim of this study was a descriptive analysis of publications that addressed the issue of termites in urban areas between the years 1945 and 2018. For the systematic review, a literature search was initiated using the ISI Web of Science (WoS), SCOPUS (Elsevier) and SCIELO databases. In total, 180 relevant studies in the field concerning urban termites were published, out of which most (58.33%) investigated about the invasive termites, followed by studies that addressed the issue of control of pest termites (28.33%) and ecology and biodiversity (13.33%). The most studied species on the invasive termites’ category was Coptotermes formosanus, which was present in 22.78% of the publications. Studies on urban termites that highlighted the importance of the control of pest termites in urban areas began in 1983. Most of them were focussed on tests with chemical products. The most tested chemical probe in different termite species was hexaflumuron. Coptotermes formosanus was the most tested, followed by Reticulitermes flavipes. The publication of studies that focus on the ecology and biodiversity of urban termites began after 1958; they compared the diversity of termites in other locations within urban areas and is distributed in a small number of papers. Some gaps in studies that may serve as suggestions for future studies and, consequently, bring new contributions and advances in the scientific knowledge of urban termites were identified and discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
Springer+ Basic
€32.70 /Month
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Buy Now
Price includes VAT (France)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Similar content being viewed by others
Research on urban ants: approaches and gaps
Article 02 April 2016
Urban ecology and biological studies in Brazilian cities: a systematic review
Article 24 January 2023
Systematic review of ecological research in Philippine cities: assessing the present status and charting future directions
Article Open access 04 March 2024
Change history
References
- Akhtari M, Nicholas D (2013) Evaluation of particulate zinc and copper as wood preservatives for termite control. Eur J Wood Wood Prod 71:395–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-013-0690-7ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Alberti M, Marzluff JM, Shulenberger E, Bradley G, Ryan C, Zumbrunnen C (2003) Integrating humans into ecology: opportunities and challenges for studying urban ecosystems. BioScience 53:1169–1179. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2003)053[1169:IHIEOA]2.0.CO;2ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Albuquerque AC, Matias GR, Oliveira MA, de Oliveira Couto AAV, Vasconcellos A (2012) Urban termites of Recife, Northeast Brazil (Isoptera). Sociobiology 59:183–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-013-0690-7ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Almeida-Neto M, Guimarães PR, Lewinsohn TM (2007) On nestedness analyses: rethinking matrix temperature and anti-nestedness. Oikos 116:716–722. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2007.15803.xArticleGoogle Scholar
- Austin JW, Glenn GJ, Gold RE (2008) Protecting urban infrastructure from Formosan termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) attack: a case study for United States railroads. Sociobiology 51:231–247 Google Scholar
- Badan EI, Regidor HA, Nunez HA, Acosta R, Gianoli E (2005) Species richness and structure of ant communities in a dynamic archipelago: effects of island area and age. J Biogeogr 32:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2004.01174.xArticleGoogle Scholar
- Baillie JE, Hilton-Taylor C, Stuart SN (2004) A global species assessment. Gland, Switzerland: the world conservation union. http://www.iucnredlist.org. Accessed 09 june 2010
- Baselg A (2010) Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 19:134–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2009.00490.xArticleGoogle Scholar
- Borges PA, Guerreiro O, Ferreira MT, Borges A, Ferreira F, Bicudo N, Myles TG (2014) Cryptotermes brevis (Isoptera: Kalotermitidae) in the Azores: lessons after 2 yr of monitoring in the archipelago. J Insect Sci 14:172. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/ieu034ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Camarota F, Powell SS, Melo A, Priest GJ, Marquis RL, Vasconcelos H (2016) Co-occurrence patterns in a diverse arboreal ant community are explained more by competition than habitat requirements. Ecol Evol 6:8907–8918.
- Chouvenc T, Su NY, Elliott ML (2008) Interaction between the subterranean termite Reticulitermes flavipes (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) and the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae in foraging arenas. J Econ Entomol 101:885–893. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/101.3.885
- Clausen CA, Yang VW, Arango RA, Green F III (2009) Feasibility of nanozinc oxide as a wood preservative. Proc Amer Wood Protect Assoc 105:255–260 Google Scholar
- Clerici DJ (2017) Efeitos de diferentes sistemas nanoestruturados de óleos essenciais em cupins subterrâneos (Coptotermes gestroi). Dissertation, Centro Universitário Franciscano
- Connor EF, Hafernik J, Levy J, Moore VL, Rickman JK (2002) Insect conservation in an urban biodiversity hotspot: the San Francisco Bay Area. J Insect Conserv 6:247–259. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024426727504ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Constantino R, Dianese EC (2001) The urban termite fauna of Brasília, Brazil. Sociobiology 38:323–326 Google Scholar
- Costa DA, Santo-Filho KDE, Brandão D (2009) Padrão de distribuição de cupins na região urbana de Goiânia. Iheringia Ser Zool 99:364–367 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Culliney TW, Grace JK (2000) Prospects for the biological control of subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae), with special reference to Coptotermes formosanus. B Entomol Res 90:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485300000031ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Davies ZG, Fullera RA, Lorama A, Irvineb KN, Simsa V, Gastona KJ (2009) A national scale inventory of resource provision for biodiversity within domestic gardens. Biol Conserv 142:761–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2008.12.016ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Disney RHL, Kistner DH (1990) Revision of the termite-parasitizing genus Dicranopteron (Diptera: Phoridae). Zool J Linn Soc-Lond 98:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1990.tb01211.xArticleGoogle Scholar
- Dreistadt SH, Dahlsten DL, Frankie GW (1990) Urban forests and insect ecology. BioScience 40:192–198. https://doi.org/10.2307/1311364ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Duarte FG, Santos GA, Rosado FR, Delariva RL, Sampaio ACF (2007) Cupins (Insecta: Isoptera) na arborização urbana da zona 1 de Maringá-PR. Rev Agr Meio Amb 1:87–100 Google Scholar
- Ernesto MV, Ramos EF, Moura FMS, Vasconcellos A (2014) High termite richness in an urban fragment of Atlantic Forest in northeastern Brazil. Biota Neotrop 14:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1590/1676-06032014005214ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Faragalla ARA, Al Qhtani MH (2013) The urban termite fauna (Isoptera) of Jeddah city, western Saudi Arabia. Life Sci J, New York 10:1695–1701. https://doi.org/10.7537/marslsj140817.01ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Fattorini S (2011) Insect extinction by urbanization: a long term study in Rome. Biol Conserv 144:370–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2010.09.014ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Ferreira M, Scheffrahn RH (2011) Light attraction and subsequent colonization behaviors of alates and dealates of the west Indian drywood termite (Isoptera: Kalotermitidae). Fla Entomol 94:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1653/024.094.0202ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Ferreira MT, Borges PA, Scheffrahn RH (2012) Attraction of alates of Cryptotermes brevis (Isoptera: Kalotermitidae) to different light wavelengths in South Florida and the Azores. J Econ Entomol 105:2213–2215. https://doi.org/10.1603/EC12240ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fontes LR Sistemática geral de cupins (1995) In: Berti Filho E, Fontes LR (Eds). Alguns aspectos atuais da biologia de cupins. Piracicaba, Fundação de Estudos Agrários Luiz de Queiroz-FEALQ pp 11–17
- Fontes LR, Milano S (2002) Termites as an urban problem in South America. Sociobiology 40:103–151 Google Scholar
- Foo FK, Othman AS, Lee CY (2011) Foo FK, Othman AS, Lee CY. Morphology and development of a termite endoparasitoid Misotermes mindeni (Diptera: Phoridae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 104:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1603/AN10115ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Foo FK, Othman AS, Lee CY (2015) Longevity, trophallaxis, and allogrooming in Macrotermes gilvus soldiers infected by the parasitoid fly Misotermes mindeni. Entomol Exp Appl 155:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/eea.12296ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Frankie GW, Ehler LE (1978) Ecology of insects in urban environments. Annu Rev Entomol 23:367–387. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.en.23.010178.002055ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Fuller RA, Irvine KN, Devine-Wright P, Warren PH, Gaston KJ (2007) Psychological benefits of greenspace increase with biodiversity. Biol Lett 3:390–394. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2007.0149ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Gaju M, Notario MJ, Mora R, Alcaide E, Moreno T, Molero R, Bach de Roca C (2002) Termite damage to buildings in the province of Córdoba, Spain. Sociobiology 40:75–85 Google Scholar
- Gotelli NJ, Mccabe DJ (2002) Species co-occurrence: a meta-analysis of J. M Diamond’s assembly rules model Ecology 83:2091–2096. https://doi.org/10.2307/3072040ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Griffiths D (2017) Connectivity and vagility determine beta diversity and nestedness in north American and European freshwater fish. J Biogeogr 44:1723–1733. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12964ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Grimm NB, Faeth SH, Golubiewski NE, Redman CL, Wu J, Bai X, Briggs JM (2008) Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 319:756–760. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1150195ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guerreiro O, Cardoso P, Ferreira JM, Ferreira MT, Borges PA (2014) Potential distribution and cost estimation of the damage caused by Cryptotermes brevis (Isoptera: Kalotermitidae) in the Azores. J Econ Entomol 107:1554–1562. https://doi.org/10.1603/EC13501ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gurevitch J, Hedges LV (1999) Statistical issues in ecological meta-analyses. Ecology 80:1142–1149. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(1999)080[1142:SIIEMA]2.0.CO;2ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Hochmair HH, Scheffrahn RH (2010) Spatial association of marine dockage with land-borne infestations of invasive termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae: Coptotermes) in urban South Florida. J Econ Entomol 103:1338–1346. https://doi.org/10.1603/EC09428ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hochmair HH, Tonini F, Scheffrahn RH (2013) The role of geographic information Systems for Analyzing Infestations and Spread of Invasive Termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae and Termitidae) in urban South Florida. Fla Entomol 96:746–755. https://doi.org/10.1653/024.096.0307ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Huy NQ, Van Hanh T, Van Quang N, My NT, Hien NT, Huyen TT, Huyen NH (2014) Species composition and damage levels of termites in three world cultural heritage sites: complex of hue monuments, hoi an ancient town, and My son sanctuary. Proceedings of the 10th Pacific-termite research group conference
- Kirton LG, Azmi M (2005) Patterns in the relative incidence of subterranean termite species infesting buildings in peninsular Malaysia. Sociobiology 46:1–15 Google Scholar
- Klangkaew C, Inoue T, Abe T, Takematsu Y, Kudo T, Noparatnaraporn N, Kirtibutr N (2002) The diversity and abundance of termites (Isoptera) in the urban area of Bangkok, Thailand. Sociobiology 39:485–493 Google Scholar
- Lee CY (2002) Control of foraging colonies of subterranean termites, Coptotermes travians (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in Malaysia using hexaflumuron baits. Sociobiology 39:411–416 Google Scholar
- Lee SH, Chon TS (2011) Effects of climate change on subterranean termite territory size: a simulation study. J Insect Sci 11:80. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.011.8001ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Leimu R, Koricheva J (2005) What determines the citation frequency of ecological papers? Trends Ecol Evol 20:28–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2004.10.010ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lenner SN (2018) Termites are no big deal and other urban myths. https://www.arrownj.com/termites-are-no-big-deal-and-other-urban-myth. Accessed 2018-3-26
- Lewis VR (1997) Alternative control strategies for termites. J Agric Entomol 14:291–307 Google Scholar
- Little NS, Blount NA, Caprio MA, Riggins JJ (2014) Survey of subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) utilization of temperate forests. Sociobiology 61:198–206. https://doi.org/10.13102/sociobiology.v61i2.198-206ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Liu W, Xu Z, Mo J (2008) Evaluation on the efficacy of an automatic alarm detector for monitoring termites (Isoptera). Sociobiology 52:119–128 Google Scholar
- Logan JW, Cowie RH, Wood TG (1990) Termite (Isoptera) control in agriculture and forestry by non-chemical methods: a review. B Entomol Res 80:309–330. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485300050513ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Lowry DE, Rollinson E, Laybourn A, Scott T, Aiello-Lammens M, Gray S, Mickley J, Gurevitch J (2013) Biological invasions: a field synopsis, systematic review and database of the literature. Ecol Evol 3:182–196. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.431ArticlePubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Mankin RW, Osbrink WL, Oi FM, Anderson JB (2002) Acoustic detection of termite infestations in urban trees. J Econ Entomol 95:981–988. https://doi.org/10.1603/0022-0493-95.5.981ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Marini M, Ferrari R (1998) A population survey of the Italian subterranean termite Reticulitermes lucifugus lucifugus Rossi in Bagnacavallo (Ravenna, Italy), using the triple mark recapture technique (TMR). Zool Sci 15:963–969. https://doi.org/10.2108/zsj.15.963ArticleGoogle Scholar
- McIntyre NE (2000) Ecology of urban arthropods: a review and a call to action. Ann Entomol Soc Am 93:825–835. https://doi.org/10.1603/0013-8746(2000)093[0825:EOUAAR]2.0.CO;2ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Mello AP, da Costa BG, da Silva AC, Silva AMB, Bezerra-Gusmão MA (2014) Termites in historical buildings and residences in the semiarid region of Brazil. Sociobiology 61:318–323. https://doi.org/10.13102/sociobiology.v61i3.318-323ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Messenger MT, Su NY (2005) Colony characteristics and seasonal activity of the Formosan subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in Louis Armstrong park, New Orleans, Louisiana. J Entomol Sci 40:268–279. https://doi.org/10.18474/0749-8004-40.3.268ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Neoh KB, Lee CY (2011) The parasitoid, Verticia fasciventris causes morphological and behavioral changes in infected soldiers of the fungus-growing termite, Macrotermes carbonarius. J Insect Sci 47:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.011.4701ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Osbrink W, Cornelius ML, Lax AR (2008) Effects of flooding on field populations of Formosan subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in New Orleans, Louisiana. J Econ Entomol 101:1367–1372. https://doi.org/10.1603/0022-0493(2008)101[1367:EOFOFP]2.0.CO;2ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Peters BC, Fitzgerald CJ (1997) Field evaluation of the effectiveness of a sleeve of stainless steel mesh to protect wooden poles against subterranean termites (Isoptera). Sociobiology 30:263–270 Google Scholar
- Popat A, Liu J, Hu Q, Kennedy M, Peters B, Lu GQM, Qiao SZ (2012) Adsorption and release of biocides with mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 4(3):970–975. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nr11691j Epub 2011 Dec 23 ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Prabhakaran SK (2001) Eastern subterranean termite management using baits containing hexaflumuron in affected University of Iowa structures (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Sociobiology 37:221–233 Google Scholar
- Protection E (2003) Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). site: http://www.thecre.com/quality/spring2003/epa.pdf. Accessed 07 Dec 2013
- Puckett RT, Espinoza EM, Gold RE (2014) Alate trap-based assessment of Formosan subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) dispersal flight phenology associated with an urbanized Barrier Island ecosystem. Environ Entomol 43:868–876. https://doi.org/10.1603/EN13223ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rebele F (1994) Urban ecology and special features of urban ecosystems. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 4:173–187. https://doi.org/10.2307/2997649ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Riegel C, Gilberg M, Freytag E, Su NY, Bordes ES (2005) Long-term protection of Madame John's legacy house from subterranean termites using hexaflumuron. Stud Conserv 50:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1179/sic.2005.50.4.267ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Sanders NJ, Gotelli NJ, Heller NE, Gordon DM (2003) Community disassembly by an invasive ant species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:2474–2477. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0437913100ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Santos MN (2016) Research on urban ants: approaches and gaps. Insect Soc 63:359–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-016-0483-1ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Santos MN, Delabie JHC, Queiroz JM (2019) Biodiversity conservation in urban parks: a study of ground-dwelling ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Rio de Janeiro City. Urban Ecosyst 22:927–942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11252-019-00872-8ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Scheffrahn RH, Hochmair HH, Kern WH Jr, Warner J, Krecek J, Maharajh B, Hickman RB (2014) Targeted elimination of the exotic termite, Nasutitermes corniger (Isoptera: Termitidae: Nasutitermitinae), from infested tracts in southeastern Florida. Int J Pest Manage 60:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670874.2014.882528ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Silva DG, Trevisan H, Carvalho AG, Resende AS, Franco AA (2009) Entomofauna associada a remanescentes de Mata Atlântica conectados por um corredor ecológico agroflorestal. Congr Bras Sist Agroflorestais 2–4
- Simms D, Husseneder C (2009) Assigning individual alates ofthe Formosan subterranean termite (Isoprera: Rhinorermitidae) to their colonies oforigin within the context ofan area-wide management program. Sociobiology 53:631–650 Google Scholar
- Spiegel MR (1976) Análise de Fourier. McGraw-Hill, São Paulo, Coleçãoo Schaum Alfredo Alves de Farias
- Su NY (1994) Field evaluation of a hexaflumuron bait for population suppression of subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J Econ Entomol 87:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/87.2.389ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Su NY (2002) Novel technologies for subterranean termite control. Sociobiology 40:95–102 Google Scholar
- Su NY, Ban PM, Scheffrahn RH (1993) Foraging populations and territories of the eastern subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in southeastern Florida. Environ Entomol 22:1113–1117. https://doi.org/10.1093/ee/22.5.1113ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Su NY, Ban PM, Scheffrahn RH (1996) An above-ground station for monitoring structure-infesting populations of the Formosan subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Sociobiology 27:39–45 Google Scholar
- Su NY, Ban PM, Scheffrahn RH (1997) Remedial baiting with hexaflumuron in above-ground stations to control structure-infesting populations of the Formosan subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J Econ Entomol 90:809–817. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/90.3.809ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Su NY, Scheffrahn RH (1998) A review of subterranean termite control practices and prospects for integrated pest management programmes. Integr Pest Manage Rev 3:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009684821954ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Sun JZ, Lockwood ME, Etheridge JL, Carroll J, Hollomon CZ, Coker CE, Knight PR (2007) Distribution of Formosan subterranean termite (Isoptera: rhinotermitidae) in Mississippi. J Econ Entomol 100:1400–1408. https://doi.org/10.1603/0022-0493(2007)100[1400:DOFSTI]2.0.CO;2ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Subekti N, Priyono B, Aisyah AN (2018) Biodiversity of termites and damage building in Semarang, Indonesia. Biosaintifika 10:176–182. https://doi.org/10.15294/biosaintifika.v10i1.12832ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Swain CR, Puckett RT, Gold RE (2011) Laboratory evaluation of feeding preferences of Formosan subterranean termites, Coptotermes formosanus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae), on cultivars of pecan, Carya illinoinensis in Texas. Sociobiology 57:191–200 Google Scholar
- Sze TW, Pape T, Toole DK (2008) The first blow fly parasitoid takes a head start in its termite host (Diptera: Calliphoridae, Bengaliinae; Isoptera: Macrotermitidae). Syst Biodivers 6:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1477200007002605ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Tabachnick BG, Fidell LS (2001) Using multivariate statistics, 4th edn. Allyn & Bacon, Needham Heights
- Terradas J (2001) Ecología urbana. Generalitat de Catalunya. Departament de Medi Ambient, Barcelona
- Terzi E, Kartal SN, Yılgör N, Rautkari L, Yoshimura T (2016) Role of various nano-particles in prevention of fungal decay, mold growth and termite attack in wood, and their effect on weathering properties and water repellency. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 107:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.11.010ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Ulrich W, Almeida-Neto M, Gotelli NJ (2009) A consumer's guide to nestedness analysis. Oikos 118:3–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0706.2008.17053.xArticleGoogle Scholar
- Ulrich W, Gotelli NJ (2013) Pattern detection in null model analysis. Oikos 122:2–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0706.2012.20325.xArticleGoogle Scholar
- Varma RV, Swaran PR (2007) Diversity of termites in a young eucalypt plantation in the tropical forests of Kerala, India. Int J Trop Insect Sc 27:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758407788458ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Vasconcellos A, Bandeira AG, Miranda CS, Silva MP (2002) Termites (isoptera) pests in buildings in João Pessoa, Brazil. Sociobiology 40:639–644 Google Scholar
- Verma M, Sharma S, Prasad R (2009) Biological alternatives for termite control: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 63:959–972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2009.05.009ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Vieau F (1996) Seasonal variation in caste proportions of the termite Reticulitermes santonensis Feytaud (Isoptera: Rhinotermidae) in an environment of western France. Ann Soc Entomol Fr 32:207–216 Google Scholar
- Ward D, Beggs J (2007) Coexistence, habitat patterns and the assembly of ant communities in the Yasawa islands, Fiji. Acta Oecol 32:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actao.2007.05.002ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Wilson MV (2009) "How to measure", in Field Methods in Vegetation Science, http://oregonstate.edu/instruct/bot440/wilsomar/Content/Index.htm, Accessed 2018-3-7
- Wright DH, Reeves JH (1992) On the meaning and measurement of nestedness of species assemblages. Oecologia 92:416e428. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317469ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Zorzenon FJ, Campos AEC (2015) Subterranean termites in urban forestry: tree preference and management. Neotrop Entomol 44:180–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-014-0269-yArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zvereva EL, Kozlov MV (2010) Responses of terrestrial arthropods to air pollution: a meta-analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:297–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-009-0138-0ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Laboratório de Fitossanidade, Instituto de Pesquisas Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro, IPJBRJ, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil Marcus Nascimento Santos
- Marcus Nascimento Santos
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This research does not involve human and/or animal participants. The manuscript has not been submitted to more than one journal for simultaneous consideration. The manuscript has not been published previously (partly or in full). No data have been fabricated or manipulated (including images) to support our conclusions.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure S1
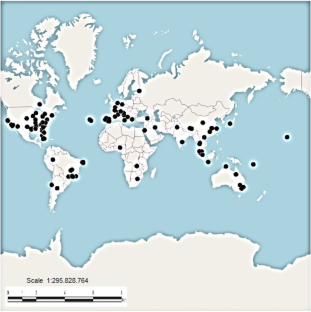
Geographic locations (black triangle) of the studies (n = 180) included in the systematic review, which were explicitly specified in the publications about urban termites published in indexed journals between 1945 and 2018. Some studies have termites sampling in more than one country (see Supplement I)(842 kb)
Supplementary Figure S2
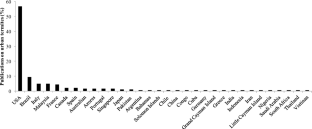
The proportion (%) of scientific articles about urban termites (n = 180) per country published in indexed journals between 1945 and 2018. *Studies with termites sampling in more than one country (see Supplement I) (44 kb)
Supplementary Figure S3
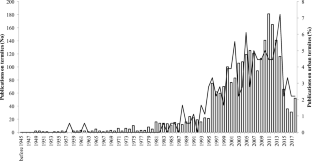
Number of scientific papers with the main theme being termites (columns) and the proportion of the number of scientific articles with the theme being urban termites (line) published in indexed journals worldwide between 1945 and 2018 (n = 2577) (37.6 kb)
Supplementary Figure S4
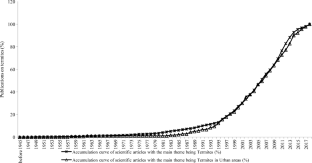
Accumulation curves of scientific articles with the main theme of termites (n = 2577) and those with the theme of urban termites (n = 180) published in indexed journals between 1945 and 2018 (72.1 kb)
Supplementary Figure S5
Accumulation curves (%) of scientific articles on urban termites (n = 180) addressed per subject category published in indexed journals between 1945 and 2018 (80 kb)








